With the holidays being upon us in no time this is a good time to remind heart patients of being acutely aware of the sodium content in foods. The holiday meal contributes to many heart patients having increased symptoms of high blood pressure, congestive heart failure, fluid retention, shortness of breath. The holiday meals can be the culprit. Traditional foods like the turkey are often injected with approximately 8% solution sodium to enhance moistness and flavor. If you read the ingredients you will often note: turkey broth, salt, sodium phosphates, sugar & flavoring. Then many a cook will soak the already salt injected turkey in a brine solution or salt it well, prior to cooking. The turkey alone gets many into trouble, then you add pre-packaged stuffing, broth, or use canned mushroom soups in casseroles. Did I mention the relish tray with pickled foods? 



A little extra salt in or on your holiday foods makes a difference.
1 teaspoon salt = 2131 mg sodium 1/2 teaspoon salt = 1066 mg sodium
1/4 teaspoon salt = 533 mg sodium 1/8 teaspoon salt = 266 mg sodium
75 mg—the average sodium content of 3 ounces fresh, unsalted beef, turkey, chicken, pork
240 mg sodium in 3 ounces self-basting frozen turkey, cooked (that’s without the gravy!)
580 mg sodium in 3 ounces frozen fully cooked baked turkey
820 mg sodium in 3 ounces honey baked ham
Bread is a major sodium contributor if you eat more than a couple of pieces a day unless you buy special low sodium bread. A slice (1 ounce) of loaf bread has 150 to 200 mg sodium—not including salted butter or other spreads or toppings. Consider using a bread maker to make a low sodium recipe.
Skip the gravy! But if you must go for low or reduced sodium gravy instead of regular salted gravy which has more than 300 mg sodium for 1/4 cup. 
Measurements and labels of sodium
- 1/4 teaspoon salt= 600 mg sodium
- 1/2 teaspoon salt= 1,200 mg sodium
- 3/4 teaspoon salt=1,800 mg sodium
- 1 teaspoon salt= 2,300 mg sodium
- 1 teaspoon baking soda =1,000 mg sodium
- Sodium-free: Less than 5 milligrams of sodium per serving
- Very low-sodium: 35 milligrams or less per serving
- Low-sodium: Less than 140 milligrams per serving
- Reduced sodium: Sodium level reduced by 25%
- Unsalted, no salt added, or without added salt: Made without the salt that's normally used, but still contains the sodium that's a natural part of the food itself.
Names for salt
- sodium alginate
- sodium ascorbate
- sodium bicarbonate (baking soda)
- sodium benzoate
- sodium caseinate
- sodium chloride
- sodium citrate
- sodium hydroxide
- sodium saccharin
- sodium stearoyl lactylate
- sodium sulfite
- disodium phosphate
- monosodium glutamate (MSG)
- trisodium phosphate
- Na
Some drugs contain high amounts of sodium.
Need an antacid after that holiday meal? Watch out there is excess sodium there too. Carefully read the labels on all over-the-counter drugs. Look at the ingredient list and warning statement to see if the product has sodium. A statement of sodium content must be on labels of antacids that have 5 mg or more per dosage unit (tablet, teaspoon, etc.). Some companies are now producing low-sodium over-the-counter products. If in doubt, ask your healthcare practitioner or pharmacist if the drug is OK for you.
How Sodium causes fluid retention
The job of the kidneys is to filter the excess sodium into the urine so that the body can get rid of it. Many with heart disease and diabetes kidneys cannot handle all the extra work. The kidneys become less efficient at filtering the blood stream. This causes excess sodium to enter the bloodstream. Sodium attracts water to it and effect known as being osmotic. Water follows the sodium and is drawn into the bloodstream. Excessive salt keeps the circulatory volume higher than it should be, creating and increased pressure in the blood stream and pressing on the blood vessel walls. The stress of the pressure on the walls creates thickening and narrowing of the vessel, leaving less space for the fluid in the blood vessels and raising resistance. The body then requires higher pressure to move blood to the organs. The heart has to pump against this high pressure system.
I equate it to trying to blow up one of those kids balloons that is turned into animal shapes. They are really tough to blow air into, your cheeks get really sore - this is the resistance of air, similar to the resistance pressure of blood in the arteries. If you stretch the balloon (relax the arteries) then there is less resistance in blowing up the balloon (filling the artery with blood). Twenty percent of the blood pumped from the heart goes first to the kidneys. High blood pressure within the kidneys cause damage to the heart and to the vascular system in the kidneys. Salt makes you thirsty so limit salty foods, especially if on a fluid restriction.
I once had a patient who lost 45 lbs simply from adhering to low sodium diet. He had a very weak heart with only 10% ejection fraction meaning very limited pumping ability. So a weak heart and sodium in the diet made him retain fluid more than most. He began to measure and count sodium with every meal for a few months and was shocked by how much sodium he consumed even though he thought he ate pretty healthy. By reading labels, doing the math every day and making changes such as eating out less, ordering special, reviewing his medication he lost the fluid and added years to his life, not to mention the improved quality of life with less shortness of breath and fatigue by easing the workload of the heart. 

According to the American Heart Association, eating more than the recommended 1500 milligrams a day puts you at direct risk of high blood pressure. Yet in America we consume an average of 3400 milligrams a day; more than twice what we should. While people with hypertension, heart and kidney disease are always advised by doctors to eat less salt, the AHA wants all of us to do this, whether or not our blood pressure is currently in the normal range. So if you are cooking or know the cook for pass this info on! 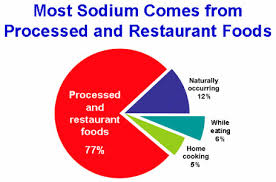



 Wall Squats
Wall Squats
 Wall push ups
Wall push ups
